Before understanding what is API we need to understand DRY( Do not repeat yourself). This means when we working with several applications which are running in different platforms like Android, IOS, Windows and different browsers we may need to configure our application to make compatible with different environments. So the same code we need to write for each environment separately.
The term API stands for ‘Application Programming Interface’. In the world of web development the term ‘API’ is synonymous with online web services which client apps can use to retrieve and update data. These online services have had several names/formats over the years such as SOAP Format, XML format, however, the current popular choice is to create a REST (or RESTful) API.
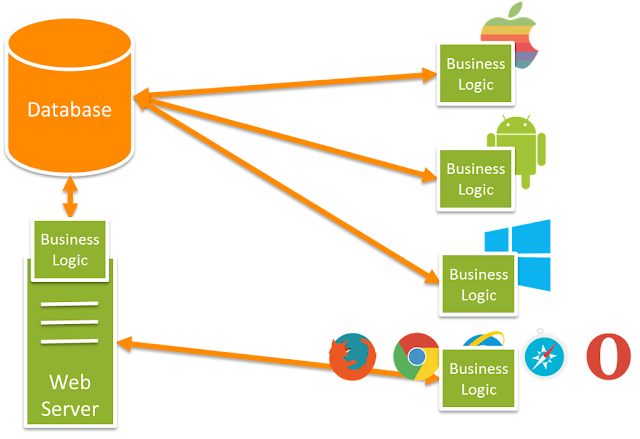
Notice that each client app has its own embedded business logic (probably written in several different languages) which connects directly to the database to get, update and manipulate data. This local business logic means that the client apps can easily become complex and all need to be maintained in sync with each other. When a new feature is required, you’ll have to update each app accordingly. This can be a very expensive process which often leads to feature fragmentation, bugs and can really give pain in your neck.
On the other hand, API is built upon REST. Now each app uses the same API to get, update and manipulate data. All apps have to feature parity and when you need to make a change you just make it in one place in line with the ‘Don’t Repeat Yourself’ (DRY) principle of software development.
In the above diagram, we can see to how RESTful service can make our life easy.

No comments:
Post a Comment